$100.00
Selank is used in clinical and experimental settings for:
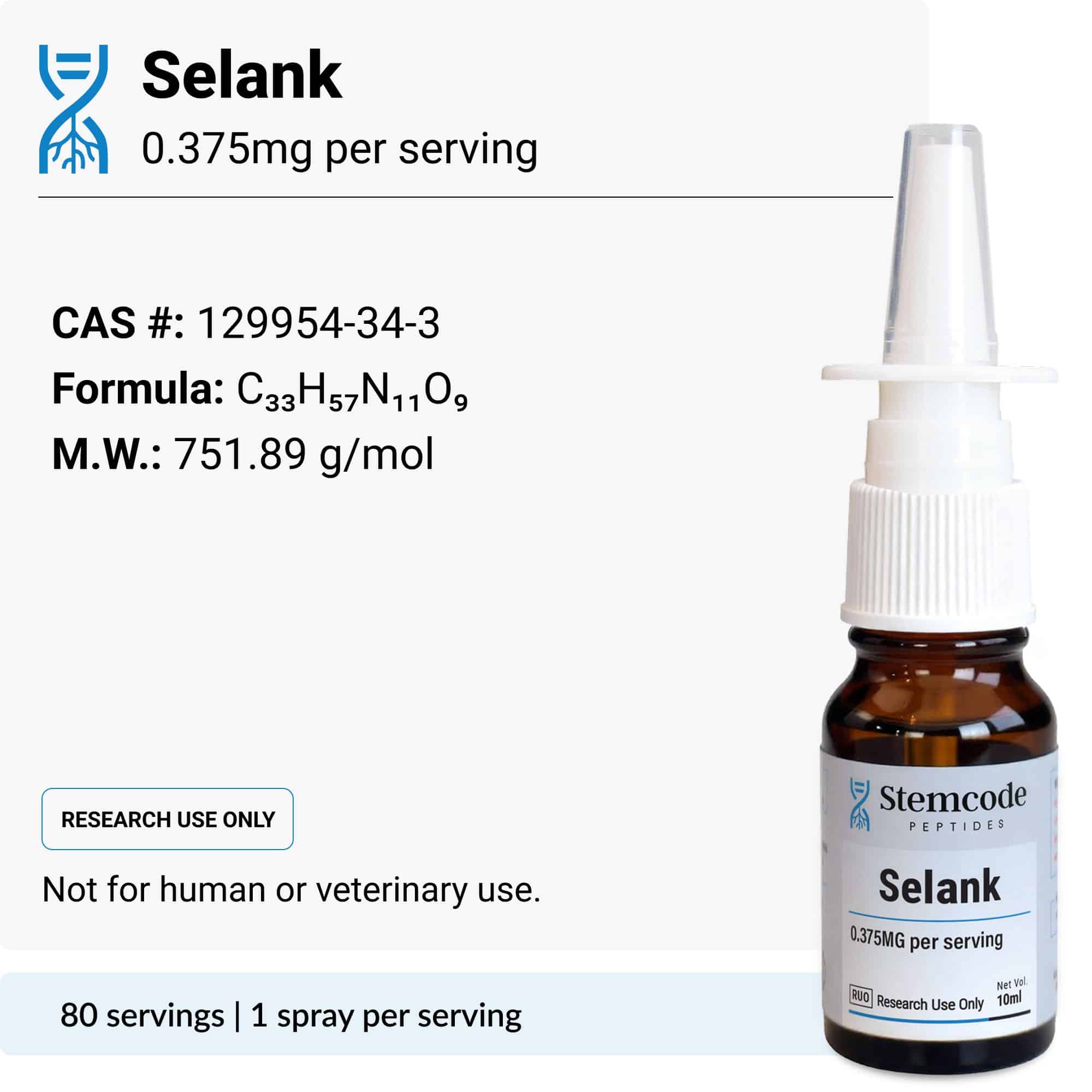
Our 10 mL Selank peptide nasal spray contains 30 mg of total peptide, releasing a precise 375 mcg dose for research purposes only. Each bottle contains 80 sprays.
Please note that all payments include a 3.99% processing fee set by our international payment processor.
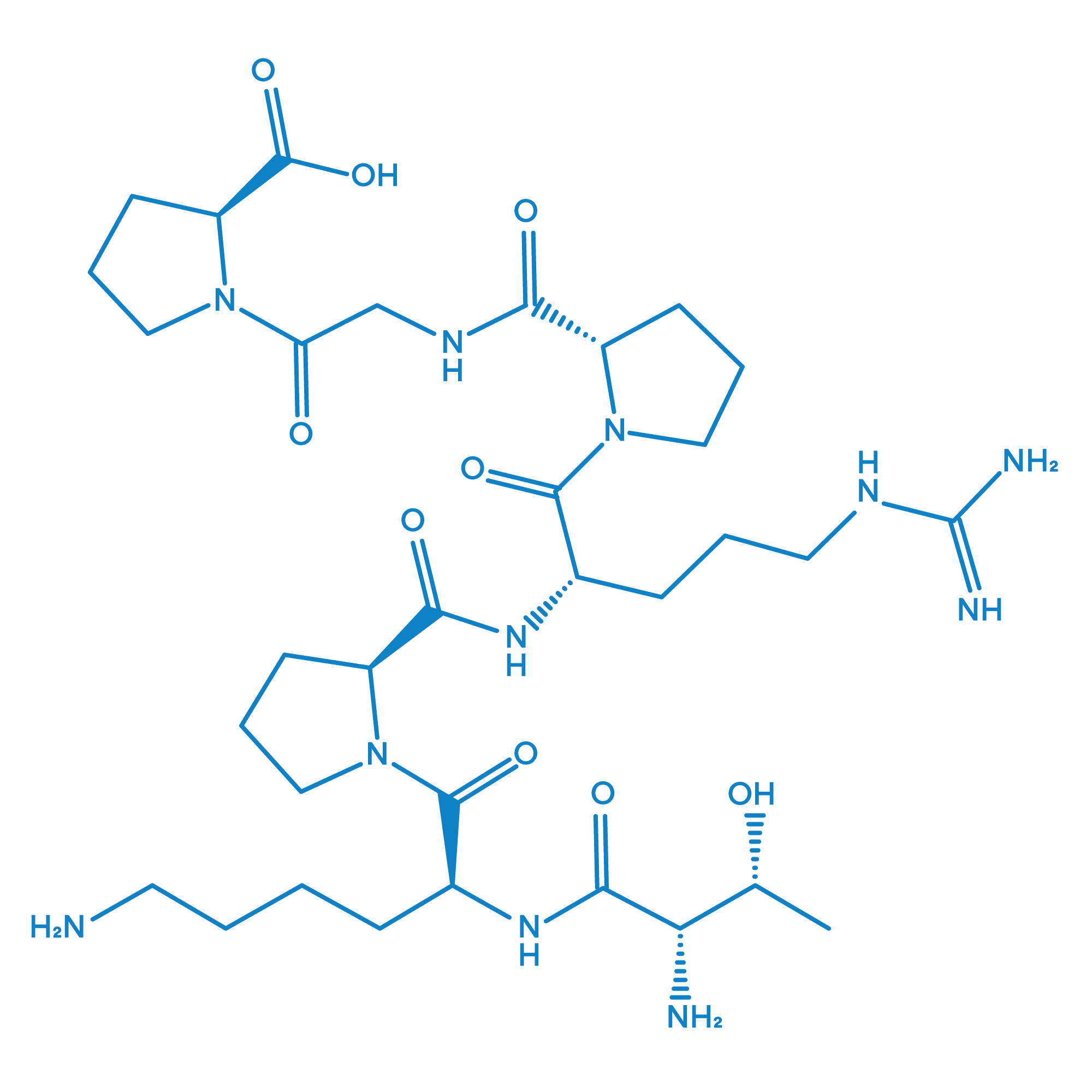
Selank is a lab-designed peptide composed of seven amino acids that resembles a natural peptide called tuftsin, which is involved in immune signalling. Researchers study Selank because it appears to affect stress, anxiety, and cognitive health.
Unlike many anxiety-related compounds like benzodiazepine, Selank doesn’t appear to cause sedation or dependence in clinical research, making it a promising alternative worth investigating.
Selank was developed explicitly for intranasal delivery, and many published studies have examined its ability to reach the central nervous system via the nasal mucosa.
Sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg-Pro-Gly-Pro
Molecular formula: C₃₃H₅₇N₁₁O₉
Molecular weight: ~748 g/mol
Form: Synthetic peptide, nasal spray
Other Ingredients: Lab-Grade Distilled Water.
Selank nasal spray is made with high-purity peptide material and undergoes in-house and third-party lab analysis to confirm:
Lab testing ensures that the material provided is consistent, high-quality, and suitable for research purposes.
Here are some highlighted areas of research related to the Selank. Please note this compound is not approved as a dietary supplement or a drug. All information below refers to published studies in clinical or animal research settings.
Selank is described as an “anxiolytic” peptide because the majority of research points to how it may influence pathways related to anxiety. In clinical trials involving general anxiety disorder (GAD), Selank improved anxiety scores compared to the placebo or medazepam, without sedation, muscle relaxation, or withdrawal [1, 2]
Selank has been shown in research to affect multiple neurotransmitter systems, such as dopamine, serotonin, and GABA, without causing sedation. Research in rats shows that Selank alters the activity of genes encoding GABA receptors, which are key components of the brain’s primary calming system. It appears to support GABA’s anxiety‑reducing effects but not in the same way as benzodiazepines, which is why it may reduce anxiety without causing intense drowsiness [3].
In animal studies, Selank was shown to alter levels of dopamine, serotonin, and related neurotransmitters in brain areas that control mood and motivation. It can raise or lower these signals in a balanced way, which may help steady emotions and stress responses rather than overstimulating the brain [4].
Selank was intentionally developed for intranasal use, and rat studies show that this route is the best for central nervous system uptake. When Selank is given intranasally, small amounts of the peptide can be detected in brain tissue, indicating that it can travel from the nasal cavity to the CNS rather than being broken down in the gut as many orally administered peptides are [3].
Can’t find what you need? Contact us and our support team will get back to you within 1–2 business days.
All products on Stemcode are intended strictly for laboratory, academic, and scientific research purposes. They are not approved for human or veterinary use.
Due to the sensitive nature of research materials used, all sales are final unless the product arrives damaged or incorrect.
No. Resale or repackaging without authorization is prohibited. Our products are solely for research.
At this moment, we ship only within the United States.
Each product page includes specific storage guidelines (e.g., refrigeration or room temperature).
Selank is a synthetic heptapeptide developed from a natural immune system fragment called tuftsin. Research explores its influence on anxiety, neurotransmitter balance, and cognitive regulation.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.